|
 Acoustic Impedance and Reflection Coefficients
Acoustic Impedance and Reflection Coefficients
Sound is reflected back toward the source of energy whenever
an acoustic impedance boundary occurs or Poisson's ratio
changes. Acoustic impedance is the product of velocity and
density. Energy is also lost due to reflection and spherical
divergence.
The SI unit of acoustic impedance is the pascal second per
cubic metre (Pa·s/m3) or the rayl per square metre
(rayl/m2), while that of specific acoustic impedance is the
pascal second per metre (Pa·s/m) or the rayl.
The basic equation is:
0: Zp = Velocity * Density
Where:
Zp = specific acoustic impedance (rayls)
Velocity of sound in the material (m/s)
Density = density of the material (kg/m3)
In terms of well log measurements, for near vertical incidence :
1: Zp1 = KD4 *
DENS1 / (DTC1 * KS3)
2: Zp2 = KD4 *
DENS2 / (DTC2 * KS3)
3: Refl = (Zp2 -
Zp1) / (Zp2 + Zp1)
4: Atten = Prod (1 - Refl
^ 2)
Where:
KD4 = 1000 for
Metric units (DENS in kg/m3, DTC in
usec/m)
KD4 = 10^6 for English
units (DENS in g/cc, DTC in usec/ft)
KS3 = 1.00 for Metric
units
KS3 = 3.281 for English
units
For
non-vertical incidence:
5: K = (Vavg - Vo) / DEPTH
6: ANGLE = Arctan
((DEPTH * X + Vo * X / K) / (DEPTH^2 + 2 * Vo * DEPTH / K - X^2
/ 4))
7: Vrat = Vc2 / Vc1
OR 7A: Vrat = DTC1 /
DTC2
8: Drat = DENS2 / DENS1
9: C = (Vrat^2 + (1 -
Vrat^2) / (Cos(ANGLE))^2) ^ 0.5
10: Refl = (1 - Vrat *
Drat * C) / (1 + Vrat * Drat * C)
The reflection coefficient will vary with incidence angle,
equivalent to a variation with offset distance. Attenuation is
seldom applied to reflection coefficient data, as synthetics are
often compared to gain equalized data, in which attenuation has
been compensated.
If
density log data is missing or cannot be used due to bad hole
conditions, an appropriate constant value or a value derived
from the empirical chart below can be used. A complete
reconstruction of the density log can be made if lithology is
known, by using the modeling equations given in earlier Section.
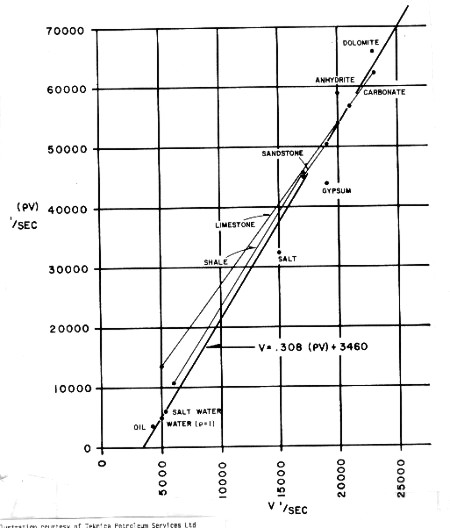
Empirical acoustic impedance from velocity
|

